Sydney-based Neara, a developer of physics-based digital twin technology for critical infrastructure, has closed an A$90 million (approximately US$63 million) Series D funding round, pushing its valuation to A$1.1 billion and establishing the company as Australia’s newest technology unicorn. The capital injection, announced on February 10, 2026, arrives as power utilities worldwide face intensifying pressure from AI-driven data center demand, aging grid infrastructure, and accelerating electrification targets.
AI Data Center Boom Drives Urgency for Grid Intelligence
The timing of the raise reflects the growing urgency facing electricity providers. According to the International Energy Agency, global electricity consumption from data centers is on track to more than double from 415 TWh in 2024 to approximately 945 TWh by 2030, roughly equivalent to Japan’s entire current annual electricity use. In the United States alone, data center power consumption could account for nearly half of all electricity demand growth through the end of the decade.
Major technology firms including Google, Microsoft, Oracle, and CoreWeave are racing to expand compute capacity for AI workloads, and the resulting strain on transmission and distribution networks has made grid optimization tools a strategic priority for utilities. Neara’s co-founder and Chief Commercial Officer Jack Curtis has noted that infrastructure systems designed for a prior era are now operating beyond their original design assumptions, and that faster, physics-grounded intelligence is needed to understand what existing networks can actually support.
TCV Leads the Round in Its Third Consecutive Neara Investment
The Series D was led by TCV, a Silicon Valley-based growth equity firm that has invested over US$20 billion in more than 350 technology companies since 1995, with a portfolio that includes Netflix, Spotify, Airbnb, and Revolut. This marks TCV’s third investment in Neara, reflecting sustained conviction in the company’s category position. Returning investors Partners Group, EQT, Square Peg Capital, and Skip Capital also participated.
The round builds on Neara’s A$45 million Series C completed in late 2024 and brings the company’s total funding to approximately A$180 million. TCV General Partner Muz Ashraf described Neara’s platform as a significant advancement in how utilities manage their grids, noting that infrastructure challenges ranging from climate resilience to energy access for AI compute demand fundamentally new approaches.
How Neara’s Physics-Enabled Platform Works
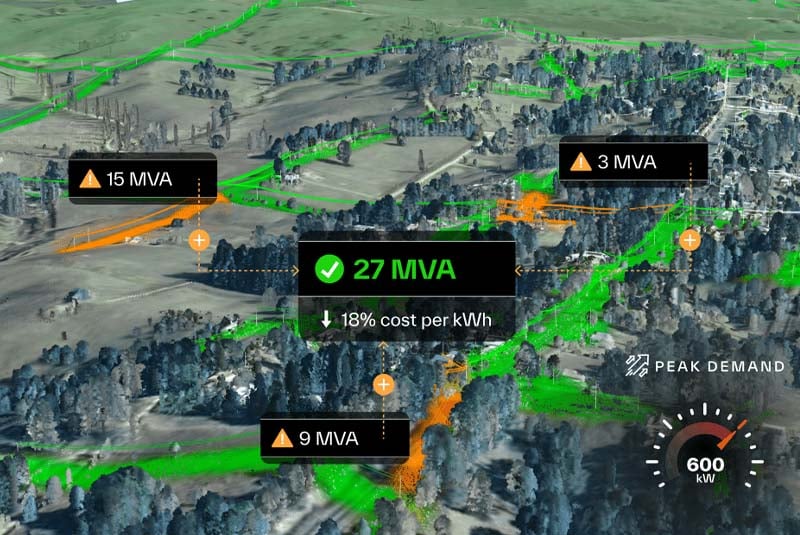
Neara, officially registered as LineSoft Pty Ltd. and founded in 2016 by Daniel Danilatos, Karamvir Singh, and Jack Curtis, builds what it calls physics-enabled digital twins. Unlike conventional mapping or statistical modelling approaches, the platform creates geometrically accurate 3D replicas of entire infrastructure networks by combining IoT sensor data, LiDAR, and AI with detailed, asset-level engineering-grade physics simulations.
The technology enables utilities to model how their physical assets, transmission lines, poles, towers, substations, behave under real-world conditions including extreme weather events, vegetation encroachment, and load changes. From these simulations, operators can identify hidden network capacity without building new infrastructure, prioritize maintenance and capital upgrades, and accelerate the connection of renewable generation sources. The company claims its approach can help utilities bring new infrastructure online up to 85% faster compared to traditional planning methods, while delivering cost savings that can reach eight- and nine-figure sums by consolidating workflows for planning, design, and vegetation management into a single platform.
Global Scale and Utility Adoption
Neara has modeled over 15 million infrastructure assets spanning more than 3 million kilometers across four continents. Its customer base includes Essential Energy and Powercor in Australia, Southern California Edison in the United States, and CenterPoint Energy, the Houston-based utility that deployed Neara’s 3D digital twin across its 8,000-square-kilometer Greater Houston service area following the devastating impact of Hurricane Beryl in 2024.
The company has also demonstrated tangible operational results through its Australian utility deployments. SA Power Networks used the platform during major flooding events to monitor clearance levels daily, enabling faster power restoration, within five days rather than the anticipated three-week timeline using manual inspection methods. Similarly, Endeavour Energy reported eliminating approximately 300 hours of inspection time by simulating flood impact through the platform rather than waiting for traditional digital inspections.
Expansion Plans Target AI Talent and International Markets
Neara intends to deploy the new capital toward two main objectives: scaling its machine learning and AI engineering workforce and deepening its international commercial presence. The company has described its goal as establishing the “physics-first” approach as a standard in infrastructure intelligence — positioning physics-based digital twins not as a specialized tool, but as the foundational layer for how modern energy, transport, and communications networks are understood and operated.
Where This Fits in the Broader Digital Twin Market
The investment comes amid growing interest in digital twin technologies across the global energy sector. In a recent high-profile deployment covered by Kurrant, National Grid and Atos launched Triton, a digital twin and data visualization platform designed to overhaul infrastructure investment planning for England and Wales, with the partners estimating a potential 70% reduction in evaluation and approval timelines for network reinforcements. In the US, PJM Interconnection, the country’s largest regional transmission operator, entered a multi-year partnership with Google and Alphabet-incubated Tapestry to build AI-powered grid planning tools.
Neara’s CenterPoint Energy partnership was also previously covered by Kurrant, when the utility deployed Neara’s technology to strengthen its network against extreme weather following Hurricane Beryl’s US$1.7 billion in damages.
With over 70 startups now active in the energy digital twin space globally, and the IEA warning that around 20% of planned data center projects could face delays unless significant transmission infrastructure investments are made, the market conditions appear to favor companies offering solutions that can extract more capacity from existing grid assets. Whether Neara can translate its unicorn valuation into sustained global market leadership will depend on how quickly it can scale beyond its current utility customer base and prove the technology’s effectiveness across different regulatory and infrastructure environments.